In Vitro Fertilisation (IVF)
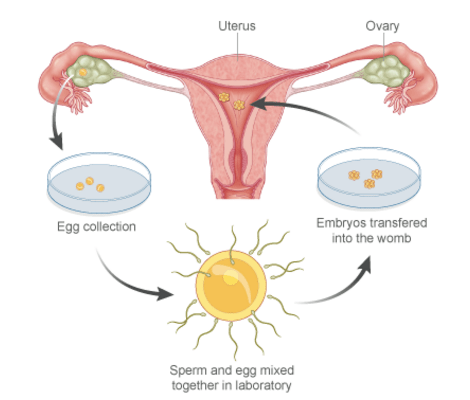
In-vitro Fertilization (IVF) is the most commonly implemented assisted reproductive technology (ART), and has helped thousands realize their dreams of parenthood. IVF is a process of fertilization where an egg is combined with sperm outside the body.
The process involves monitoring and stimulating a woman’s ovulatory process, removing an ovum or ova (egg or eggs) from the woman’s ovaries and letting sperm fertilize them in a laboratory. The fertilized egg (zygote) undergoes embryo culture for 2 – 5 days, and is then transferred to the same or another woman’s uterus, with the intention of establishing a successful pregnancy. IVF may be used to overcome female infertility where it is due to problems with the fallopian tubes, making in-vivo fertilization difficult. It can also assist in male infertility, in those cases where there is a defect in sperm quality.
Steps Involved:
- Ovarian hyperstimulation for follicle development
- Egg retrieval
- Sperm collection
- Fertilization
- Embryo development
- Embryo transfer
- Pregnancy test
Egg Retrieval and Egg Scanning
Egg Retrieval is done under Transvaginal Ultrasound guidance under general anesthesia in the operation room.

The eggs retrieved are sent through the hatch into the IVF lab where the Egg Scanning is carried out by a qualified Embryologist.

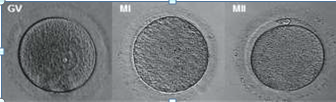
Human Oocytes: GV, MI & MII
Fertilization, Embryo Development & Laser Assisted Hatching in IVF Lab

Who might benefit?
- Female with damaged or blocked fallopian tubes, or structural defects (congenital abnormalities) of the uterus
- When the ovaries do not respond to infertility medications.
- For females with luteinized unruptured follicles
- When male partner has low sperm count or poor sperm motility or poor survival rate
- Immunological factors
- The women has significance Endometriosis leading to infertility
- When the infertility is “unexplained” Success Rates
- IVF Success Rate is the percentage of all IVF procedures which result in favorable outcomes. Depending on the type of calculation used, this outcome may represent the number of confirmed pregnancies, called the Pregnancy Rate, or the number of live births, called the Live Birth Rate.
- The success rate depends on variable factors such as maternal age, cause of infertility, embryo status, reproductive history and lifestyle factors.
- The procedure has an average success rate of 30 – 35%. This rate is affected by the women’s age at the time of treatment and upon their particular fertility problem.